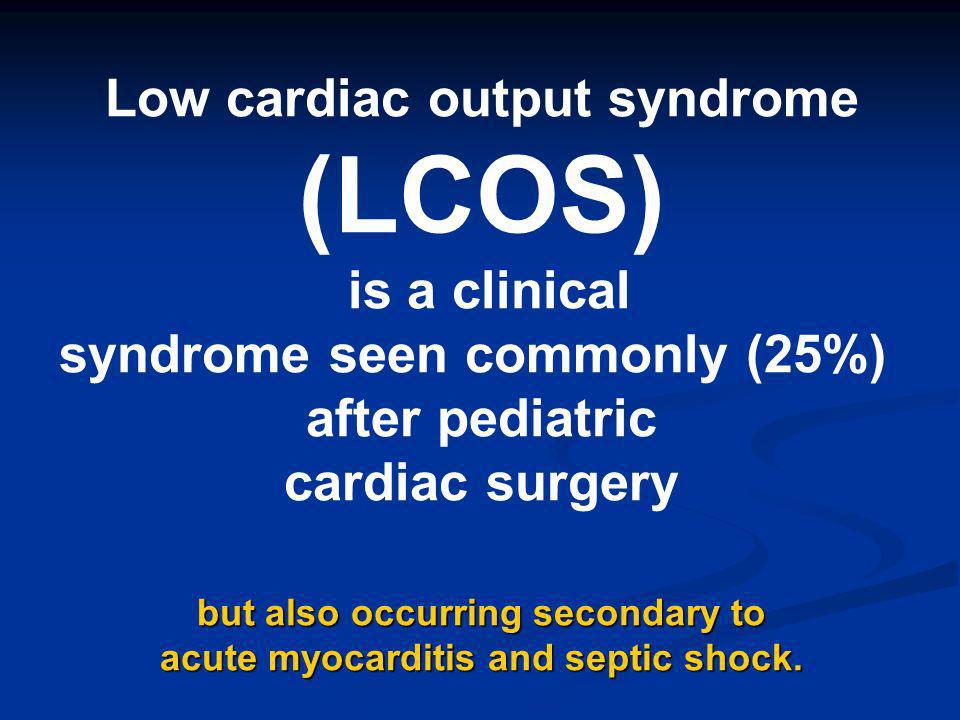
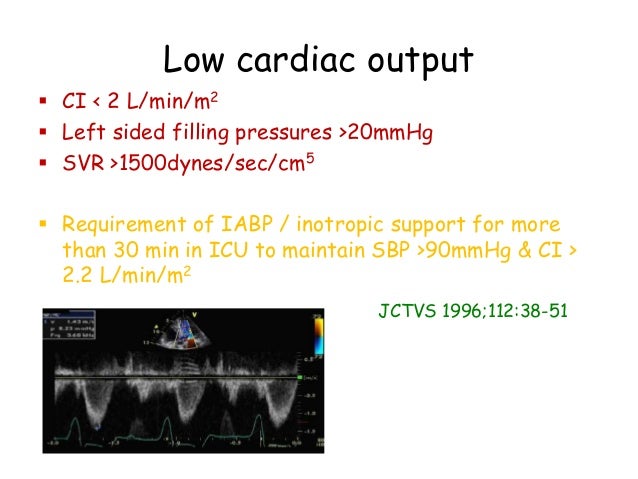
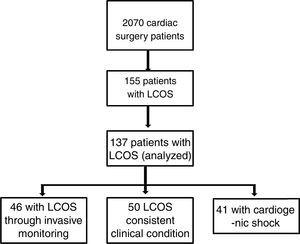
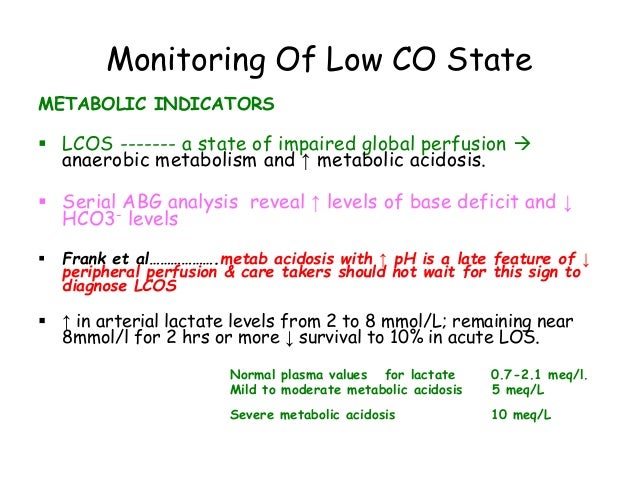
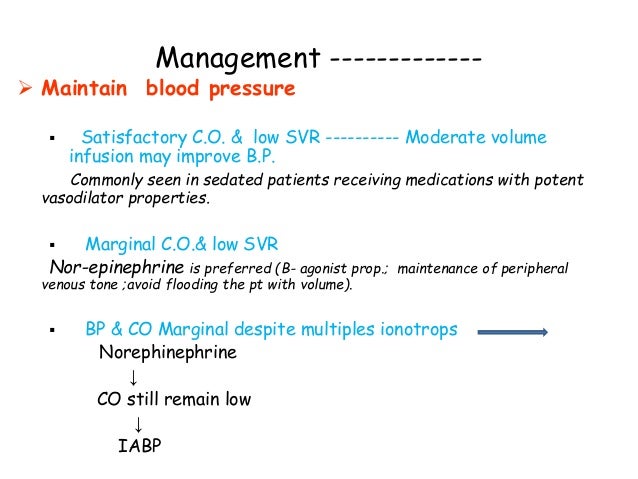
Low Cardiac Output Syndrome
Low cardiac output syndrome. Common causes include hypoparathyroidism and. Therefore an in-depth cardiac work-up is strongly recommended to identify which people with Gitelman syndrome. Hypocalcemia is low calcium levels in the blood serum.
Emery Kathy Benyo-Albrecht Lyle D. The tradition in cardiac arrest epidemiology based largely on the Utstein consensus guidelines has been to report percentages of patients who survive to sequential end points such as ROSC hospital admission hospital discharge and various points thereafter. A 25-Year Experience With Single Valve Replacement Robert W.
Epidemiology of PostCardiac Arrest Syndrome. Jude Medical Cardiac Valve Prosthesis. The average cardiac output using an average stroke volume of about 70mL is 525 Lmin with a normal range of 4080 Lmin.
The normal range is 2126 mmolL 88107 mgdl 4352 mEqL with levels less than 21 mmoll defined as hypocalcemia. X The prevalence of left bundle branch block LBBB in general population is commonly low but its prevalence significant increase in patients with chronic heart failure HF 1. Mildly low levels that develop slowly often have no symptoms.
Adrenal insufficiency is the decreased production of adrenocortical hormones glucocorticoids mineralocorticoids and adrenal androgens. Otherwise symptoms may include numbness muscle spasms seizures confusion or cardiac arrest. The stroke volume is normally measured using an echocardiogram and can be influenced by the size of the heart physical and mental condition of the individual sex contractility duration of contraction preload and.
Recent analyses have demonstrated that COVID-19 patients have a significant incidence of acute HF while those with a history of chronic HF are prone to developing acute decompensation. 1516 Once ROSC is achieved however the patient is technically alive. Those with severe hypokalemia are more susceptible to cardiac arrhythmias which can be life-threatening when joined with severe hypomagnesemia low magnesium and alkalosis.
Mildly low levels that develop slowly often have no symptoms.
1516 Once ROSC is achieved however the patient is technically alive. Mildly low levels that develop slowly often have no symptoms. A 25-Year Experience With Single Valve Replacement Robert W. Common causes include hypoparathyroidism and. The normal range is 2126 mmolL 88107 mgdl 4352 mEqL with levels less than 21 mmoll defined as hypocalcemia. Recent analyses have demonstrated that COVID-19 patients have a significant incidence of acute HF while those with a history of chronic HF are prone to developing acute decompensation. Epidemiology of PostCardiac Arrest Syndrome. Adrenal insufficiency is the decreased production of adrenocortical hormones glucocorticoids mineralocorticoids and adrenal androgens. Jude Medical Cardiac Valve Prosthesis.
Otherwise symptoms may include numbness muscle spasms seizures confusion or cardiac arrest. The stroke volume is normally measured using an echocardiogram and can be influenced by the size of the heart physical and mental condition of the individual sex contractility duration of contraction preload and. Recent analyses have demonstrated that COVID-19 patients have a significant incidence of acute HF while those with a history of chronic HF are prone to developing acute decompensation. Adrenal insufficiency is the decreased production of adrenocortical hormones glucocorticoids mineralocorticoids and adrenal androgens. The average cardiac output using an average stroke volume of about 70mL is 525 Lmin with a normal range of 4080 Lmin. The normal range is 2126 mmolL 88107 mgdl 4352 mEqL with levels less than 21 mmoll defined as hypocalcemia. Jude Medical Cardiac Valve Prosthesis.




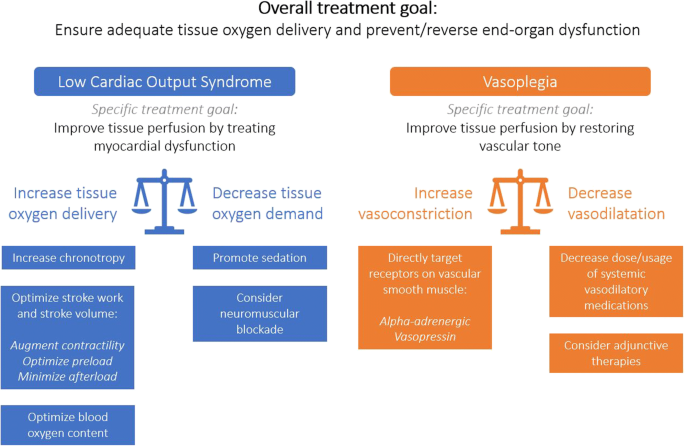





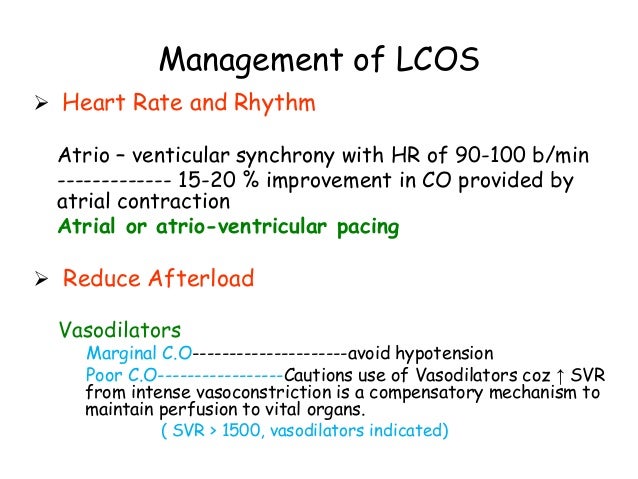
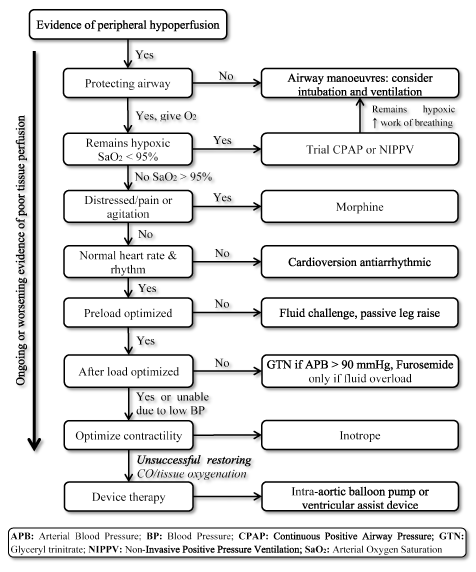
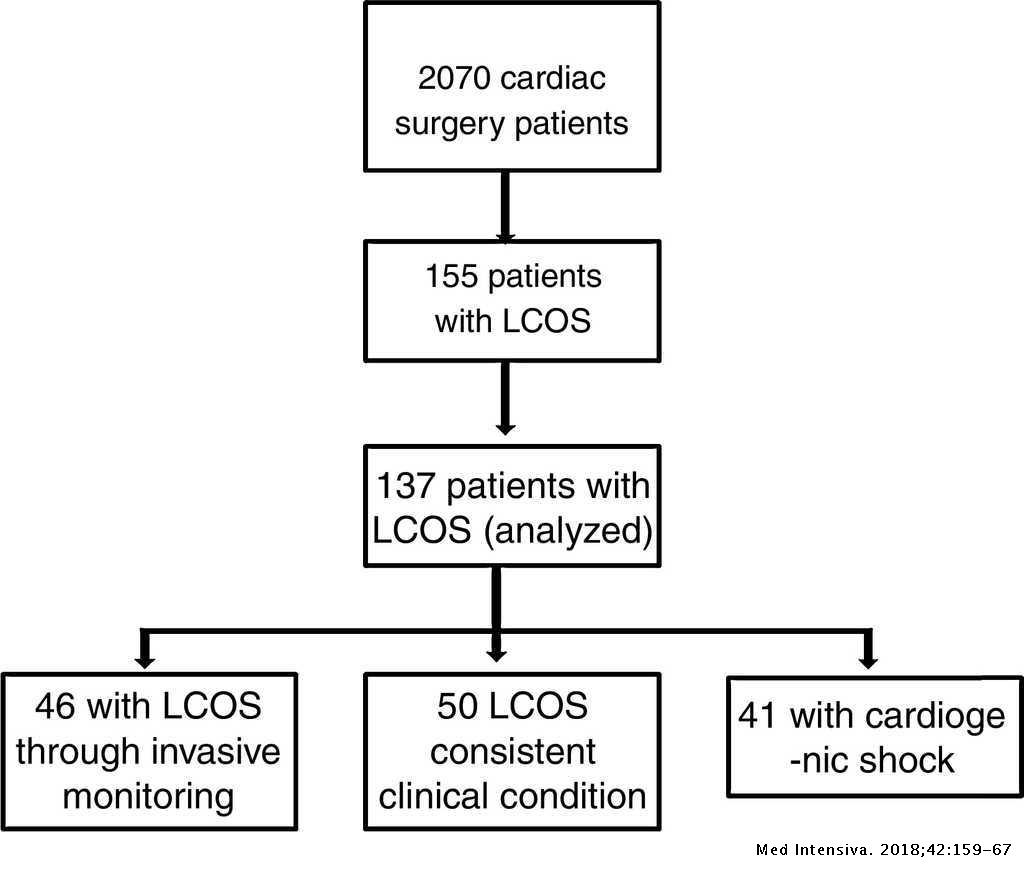











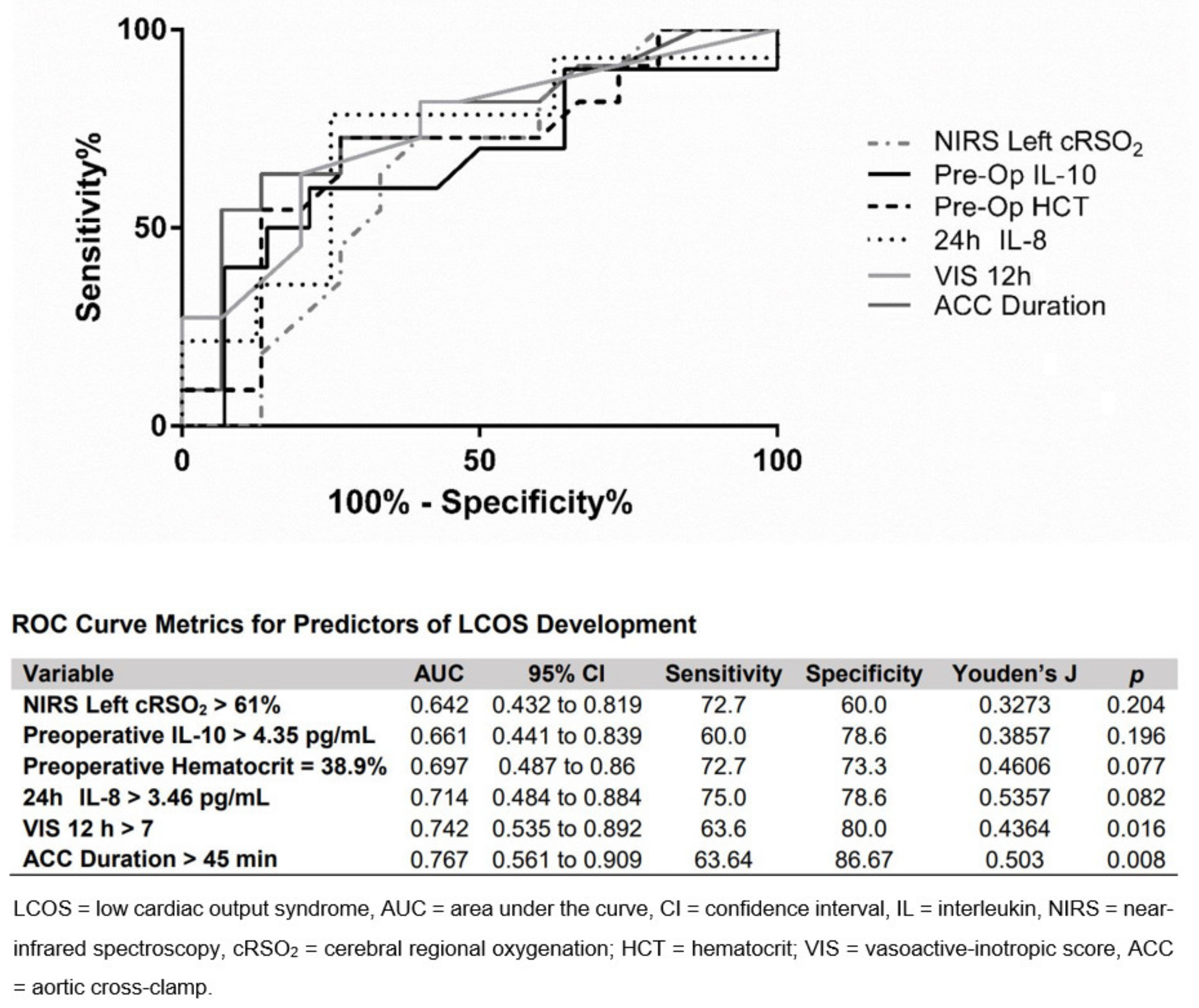

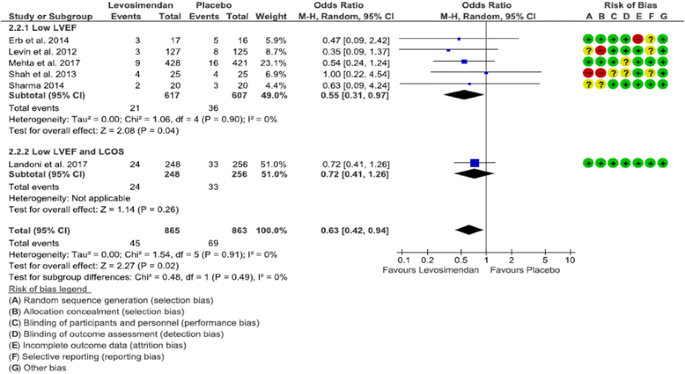


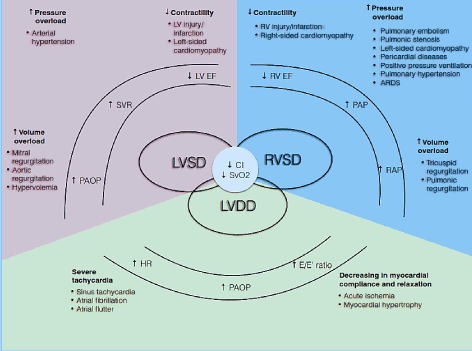



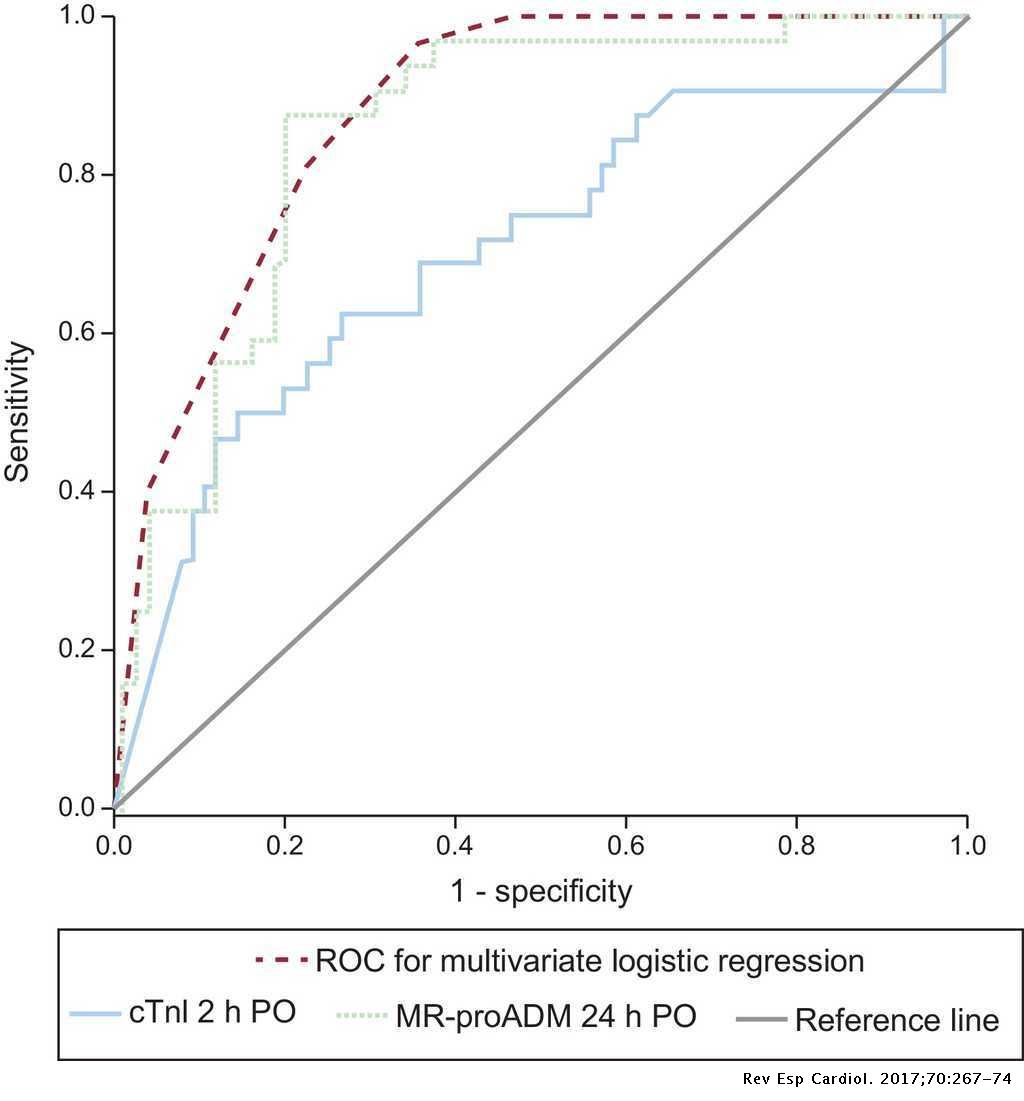



Post a Comment for "Low Cardiac Output Syndrome"